The Steel Wire has invited Park Jong-jae, a motorsport columnist, to explore light weighting trends in the automotive industry and how POSCO GIGA STEEL represents the next evolution in lightweight material design.
Automakers Work Toward Lightweighting
Traditionally, adding strength to a material meant adding thickness as well. As expected, when the material becomes thicker, the car gets heavier. However, manufacturers are introducing new technologies that challenge these commonly held notions. In fact, automotive materials are becoming thinner and lighter, while still retaining the same level of strength.

Renault Samsung’s SM6 (Talisman) is more spacious and lightweight than its competitors. (Image courtesy of Renault Samsung)
Thanks to new lightweight materials, cars can be stronger, lighter, and more spacious – three conditions that were once considered mutually exclusive. For years, people tried discovering ways to decrease a car’s weight while increasing its strength by experimenting with various metals such as aluminum, magnesium, beryllium, and other complex materials. As a result, vehicles today can weigh less compared to older models while retaining superior performance and more spacious design.
Light weighting trends first began in the aerospace industry as they needed to develop more lightweight aircraft and spacecraft. Race car designers quickly followed in order to maximize output that would allow cars to make faster turns while also improving fuel efficiency. Today, the same technologies used in race cars from 20-30 years ago are being used in mass production vehicles to improve fuel consumption, lower CO2 emissions, and increase safety.

The motorsport industry was the ideal place to develop lightweight materials as it was constantly searching for stronger, safer, and more efficient cars.
Finding the Right Balance with Lightweight Materials
Depending on their role, the bones that make up the human body consist of different strengths, densities, and elasticities. Similarly, the strength and design of auto parts must be adapted to where it fits within the car. Like the skeleton of a human being, the frame of a car is very complex. The strength and design of each of those parts play a role in how lightweight and safe the vehicle can be. While automotive manufacturers have been developing lighter materials to make vehicles stronger, more lightweight, and thinner – applying the technology can be quite difficult.
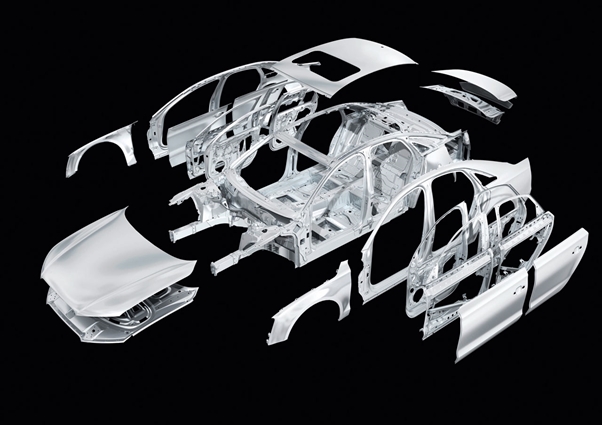
The strength and design of each auto part plays an important role in the overall weight and safety of a vehicle. (Image courtesy of Daimler AG)
Similar to how the human skull needs to be hard to protect the brain and the rib cage needs to be flexible to bend with the expansion of the lungs, parts of a car need to be built with a specific purpose. Some parts need to be built with high strength materials, while others need to be made with steel that can flex on impact. If cars were built with all strength and no shock-absorbing features, all of the kinetic energy from a crash would be absorbed by the people inside the car. On the contrary, if all car frames were only built to absorb collisions, the exterior of the car could easily fall apart and injure passengers.
Several considerations should be made when working with lightweight materials, with the first being cost. The materials that go into making space shuttles or race cars are often expensive and yield high production costs. Higher costs for the manufacturer mean higher costs for the consumer and despite the benefits that come with lighter materials, consumers will ultimately find it an unreasonable alternative. Another problem in working with some lightweight materials is that they require advanced technologies to shape, join, or weld.
This is why POSCO GIGA STEEL is proving to be a revolutionary new concept in material light weighting. It meets the demanding criteria for car frames by being lighter, harder, and more efficient overall than other competing materials.
POSCO GIGA STEEL and Its Applications
POSCO GIGA STEEL gets its name from its tensile strength, which is over 1,000MPa (megapascal), or 1GPa (gigapascal).
“A 1 square centimeter plate of POSCO GIGA STEEL can support the weight of 10 tons without becoming damaged in any way.”

POSCO GIGA STEEL gets its name from its tensile strength, which is over 1,000MPa (megapascal), or 1GPa (gigapascal).
While POSCO GIGA STEEL has excellent strength properties, it is also extremely lightweight and formable. This means car makers have more freedom to create complex auto parts with the right strength and flexibility for a specific part of the car.
Aluminum is also lightweight but POSCO GIGA STEEL is more than three times stronger. Increasing the strength of a material while making it possible to use thinner pieces is a major breakthrough that came about through many years of research.
Critical differences between POSCO GIGA STEEL and aluminum can also be found in their production processes. Manufacturing POSCO GIGA STEEL does not require welding or adhesives like other lightweight materials, and this simpler production process ultimately leads to more cost-effective prices for consumers.

SsangYong Motor’s G4 Rexton reduced the weight of the car frame while maintaining the structural advantages of the body-on-frame chassis (Image Courtesy of SsangYong Motor).
One of the manufacturers that have benefited from POSCO GIGA STEEL is SsangYong Motor. SsangYong Motor’s G4 Rexton features a traditional body-on-frame chassis as opposed to the more commonly used monocoque chassis in which a vehicle’s body and frame are one integrated structure. Although the body-on-frame chassis is structurally strong and, it is usually heavier and less efficient. However, through its research and collaboration with POSCO, SsangYong Motor was able to reduce the weight of the car frame while maintaining the structural advantages of the body-on-frame chassis by using POSCO GIGA STEEL (1.5GPa).
The biggest advantage of POSCO GIGA STEEL is that it delivers a clear solution for complex chassis structures and satisfies several different requirements in the automotive industry. Various manufacturers are currently working with POSCO to learn how they can apply POSCO GIGA STEEL to their cars.
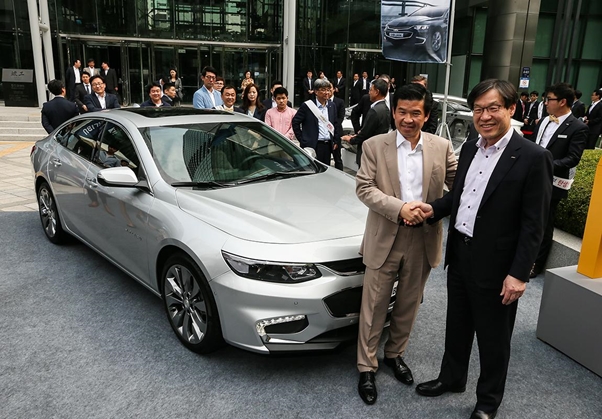

GM Chevrolet also partners with POSCO to overcome the increasingly strict regulations in the automotive industry.
The auto industry has long been working to improve emissions and safety standards. In a market environment that continues to pursue stricter standards, POSCO is committed to working with automakers to give them the most advanced material solutions for improved efficiency and safety.
Throughout April, The Steel Wire has shared insights into the current and forthcoming trends in the automotive industry. In May, we will explore how innovative steel products like POSCO GIGA STEEL can help drive the future of the automotive industry through the eyes of industry experts.
| Park Jong-jae is a motorsport columnist and the former editor-in-chief at F1 Racing Korea. |
Don’t miss any of the exciting stories from The Steel Wire – subscribe via email today.
