‘Smart Factory’ is a milestone for the manufacturing industry today. It is an intelligent production plant that improves productivity, quality, and customer satisfaction by applying core technologies of the Fourth Industrial Revolution — including Artificial Intelligence, Big Data, and the Internet of Things. To accelerate the smartization of the manufacturing industry, the World Economic Forum announces companies that have successfully established a smart factory as a ‘Lighthouse Factory’ every January and July. POSCO became the first Korean company to enter the list in July last year.
However, the Lighthouse Factory POSCO does not stop at simply leading the introduction of the Fourth Industrial Revolution technologies. What’s more? Here are the three factors that make POSCO stand out.
① Challenging the Impossible — POSCO’s Smart Blast Furnace
An unmanned storehouse or an automotive parts assembly factory run by robots could be the first thing that comes to mind when one hears the word ‘AI factory.’ Another might think that Artificial Intelligence could be applied only in specific areas, like the information technology industry. A blast furnace is a gigantic facility with a height equivalent to a 40-story building. On the inside, it is full of a mixture of solids and liquids, so turning it off or ‘looking’ inside seems impossible. Due to these many factors, applying AI to a blast furnace and making it ‘smart’ was considered nearly impossible.
POSCO stood up to this challenge. In 2016, the term ‘Fourth Industrial Revolution’ began to take its place in the industry. POSCO was one step ahead, but not in a hurry. It moved on to Step-by-step digitization and smartization with caution and care. At first, POSCO tried to do this with the technology of a global IT company but did not get satisfactory results. The new technology alone wasn’t enough. However, when POSCO’s unique expertise, intuition, and knowledge — along with its field experts — were combined with it, the advanced AI blast furnace could be born.
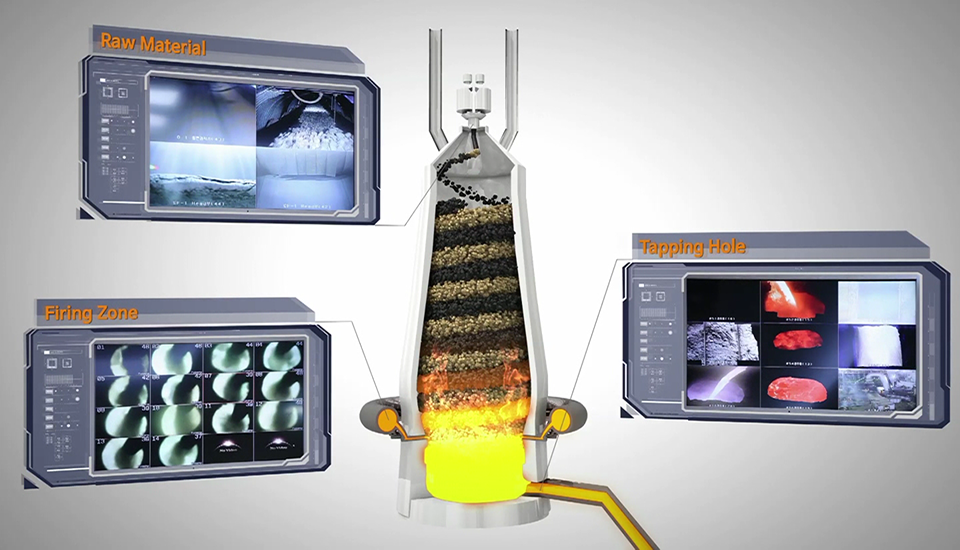

▲ The AI blast furnace is made with the combination of vast, sophisticated data, and the experience and intuition of POSCO experts. Deep learning enables optimal results and automates them to reduce human errors and increase productivity.
POSCO field experts — the technicians and engineers — standardized the main variables that determine the state of the blast furnace into Big Data. They enabled the blast furnace to conduct deep learning to extract optimal result value by imitating their know-hows accumulated for over 30 years. Facilities were also steadily improved so that the IoT could replace the manual work. As a result, POSCO boosted the daily production of molten iron by 240 tons. Additionally, workers could focus on advanced work for more creative performance. POSCO saved 250 billion KRW by carrying out 321 smart tasks — including the AI blast furnace — for the past four years.
Through the AI blast furnace, POSCO was able to break away from the old concepts of steel mills. POSCO’s “Technology for the automated control of blast furnace based on deep learning AI” is currently registered and protected as the National Core Technology of Korea (August 2019). POSCO is currently establishing smart factories not only in the blast furnace but also in the overall steelmaking, rolling, and surface treatment process and is creating high-quality smart steelworks.
② POSCO Smart Factory: A Collaboration Of Academia, SMEs, And Start-ups
There is another special feature behind the Lighthouse Factory POSCO — the collaboration of academia, SMEs, and startups in establishing the Smart Factory. As seen below, the World Economic Forum acknowledged POSCO’s effort in forming the collaboration model.
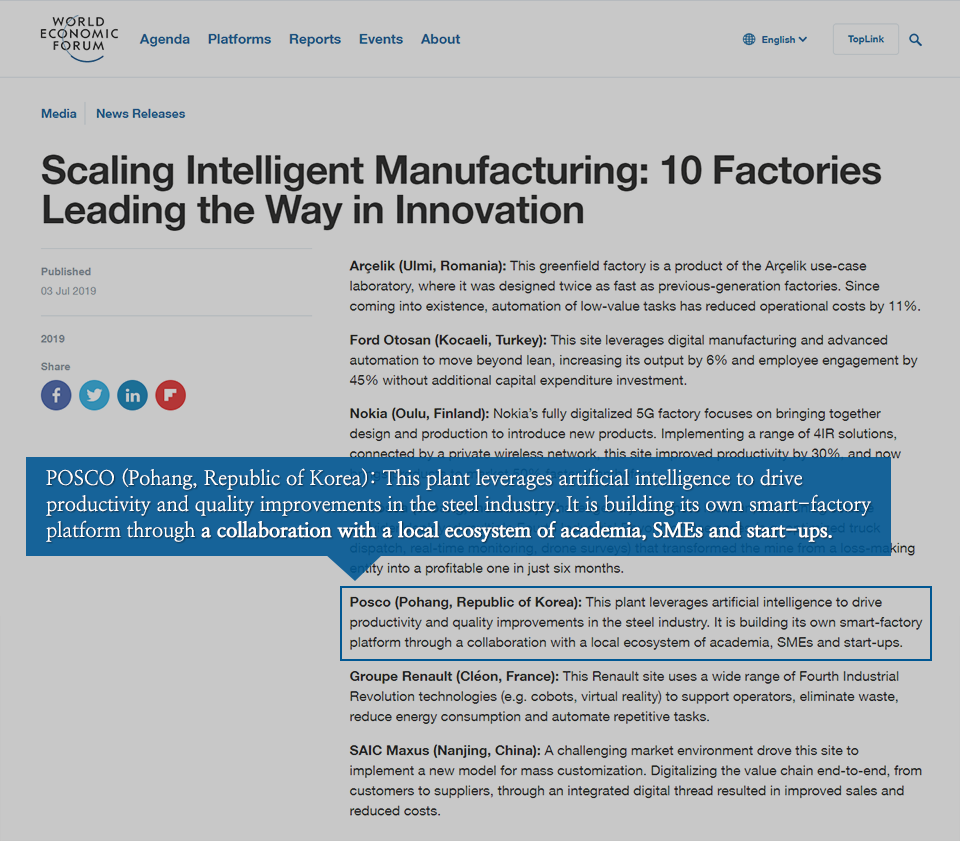
▲ A World Economic Forum article stating the reason POSCO was chosen as a Lighthouse Factory.
POSCO is actively cultivating AI experts in-house and is working with POSTECH for the cause. POSTECH has the best faculty of the artificial intelligence field in Korea. POSCO AI Expert Course, which began in 2017, is a program where selected outstanding POSCO personnel receive training from POSTECH professors. This course has resulted in more than 60 POSCO AI experts in three years. These AI experts are working to build smart factories in the work field.
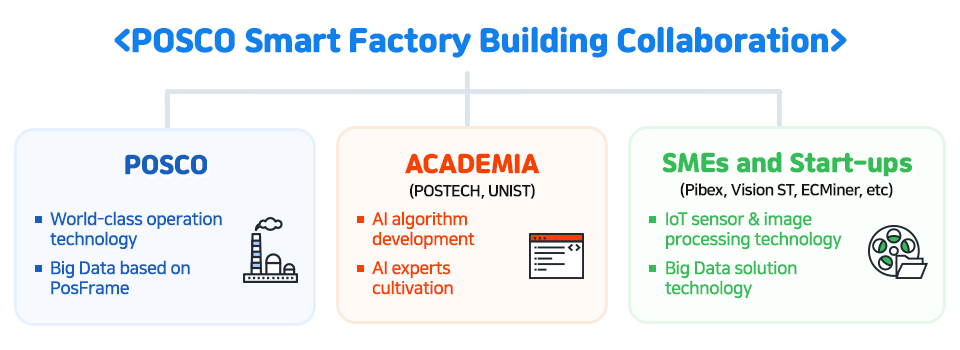
The collaboration included SMEs and start-ups as well. POSCO developed the AI blast furnace with ‘ECMiner’ since 2016. ECMiner is an SME specializing in data mining*. It created a system that can automatically identify, analyze, and maintain the combustion condition of the blast furnace by combining its data mining technology with POSCO’s accumulated data. In the past, the combustion status was left to the manual labor of workers, checking through the wind hole, and judging by experience. However, with this system, the data can now be taken care of automatically. It also maintains the appropriate combustion level of the blast furnace, which reduces the amount of coal injected. This enables an overall cost reduction.
*Data mining: A technology that looks for hidden, valid, and potentially useful patterns in huge data sets, extracts feasible information, and makes decisions accordingly.
The collaboration resulted in a win-win for both POSCO and ECMiner. POSCO succeeded in creating an AI furnace with Korean technology, and ECMiner also benefited from the experience of processing huge amounts of data at POSCO. All academia, SMEs, and start-ups that participated in the building of POSCO Smart Factory, including ECMiner, can help construct a new one in another factory based on technology experienced at POSCO. This is expected to accelerate the proliferation of smart factories in Korea.
③ Sharing With The Industrial Ecosystem
The Lighthouse Factory POSCO shines brighter for the third factor. On January 9, Korean president Jae-in Moon visited POSCO Pohang works. POSCO CEO Jeong-Woo Choi said:
“With the Smart Factory, POSCO has reduced production cost of 250 billion KRW for four years. And to relieve the wage gap with business partners, POSCO has extended an additional 270 billion KRW to outsourcing expenses for the last three years. Increased outsourcing expenses raises overall costs. However, POSCO is offsetting this through endless innovation. Through these measures, POSCO aims to foster the competitiveness of the whole industrial ecosystem, and then, in turn, enhance national competitiveness. POSCO’s management philosophy lies here.”

▲ Image source: KTV Youtube video
POSCO willingly shared the achievements of the smart factory project to solve the real problems many partner companies face. At first glance, this might simply seem like a ‘generous side’ of a large company, but in reality, this wasn’t an easy step. POSCO made this possible with its capacity earned through intense internal innovation. This is a good example showing how POSCO innovation isn’t just about POSCO.
POSCO went on to expand the benefits to SMEs who do not have direct business with POSCO. With the support service to build Smart Factory for shared growth, POSCO has provided the Smart Factory technology to 110 SMEs last year alone — 59 of which are companies with no direct business. The service will support 1,000 SMEs by 2023, with no limits to the subject. This is expected to increase the competitiveness of SMEs, which will, in turn, improve productivity and create new jobs.
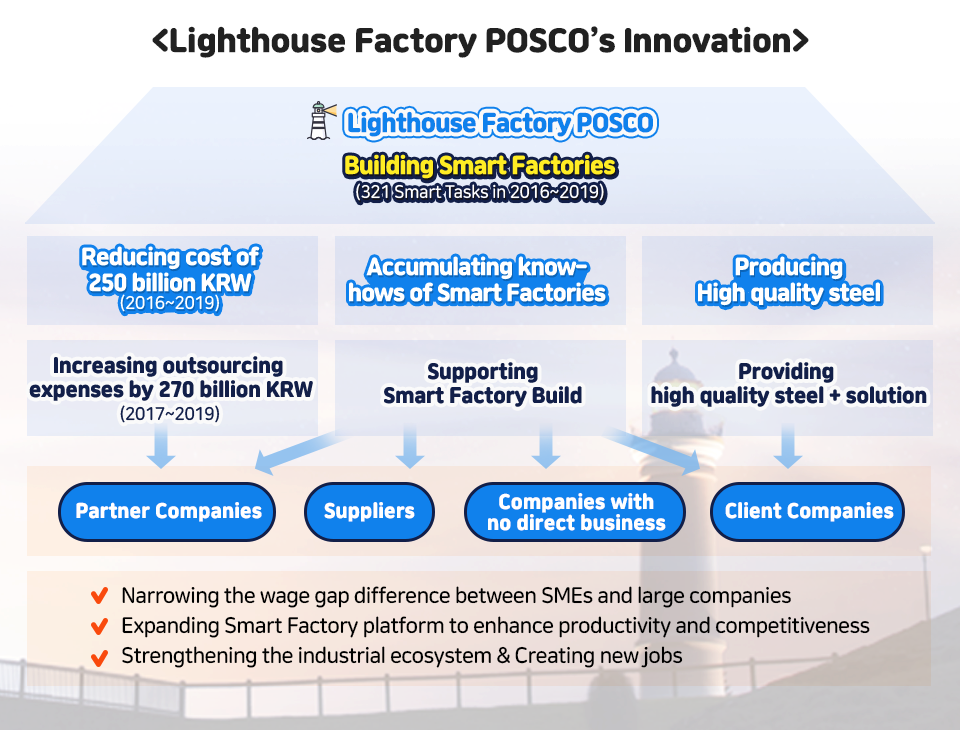
▲ POSCO’s Smart Factory project not only increases POSCO’s competitiveness but also empowers the entire industrial ecosystem. It also helps in resolving current issues like narrowing the wage gap and creating new jobs.
This is what POSCO’s innovation is all about. The willingness to share with something that was earned hard. POSCO the lighthouse factory is indeed shining the light to a brighter future of the manufacturing powerhouse Korea.
