
POSCO Group does its best to develop technologies that contribute to safety and carbon neutrality. We introduce POSCO Group’s excellent new technologies to create a better world! In this episode, we will learn about POSCO Future M’s localized technology for artificial graphite anode materials.

Graphite, which is familiar from pencil lead, is widely used in various industrial applications including refractories in converters that must withstand high temperatures. It is also a core anode material that determines the lifespan and charging performance of lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles.
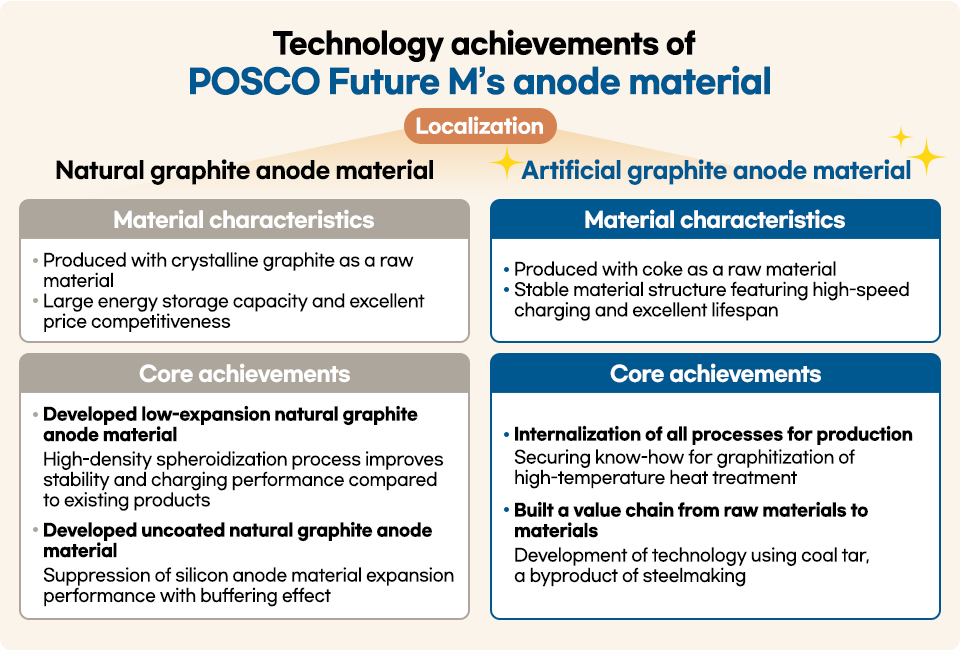
POSCO Future M is the only company in Korea that produces both anode and anode materials, which are core materials for secondary batteries. While the company was producing natural graphite anode materials made from natural graphite, it developed the technology to produce artificial graphite anode materials. POSCO Future M’s artificial graphite anode manufacturing technology processes needle coke, a raw material, at a high temperature of over 3,000 ℃ to produce anode material. It was the first Korean company to develop and commercialize artificial graphite anode production technology, which has increased the competitiveness of the domestic secondary battery industry. Why did the company develop technology for localizing artificial graphite, and what has the technology development changed?

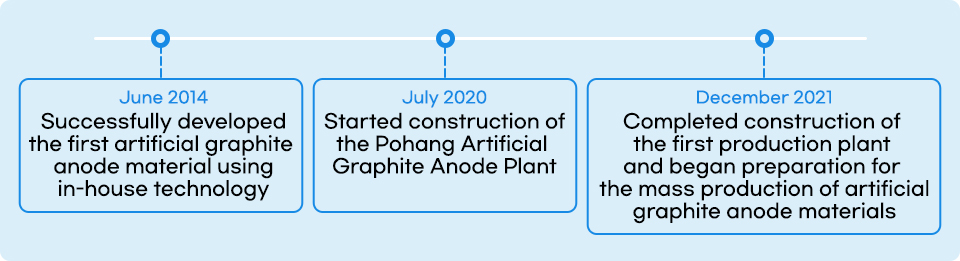

POSCO Future M entered the anode material business after realizing that coal tar, a byproduct of the steelmaking process, can be used to produce anode materials. With continuous technology development, it became the only Korean company to produce natural graphite anode materials in 2011.
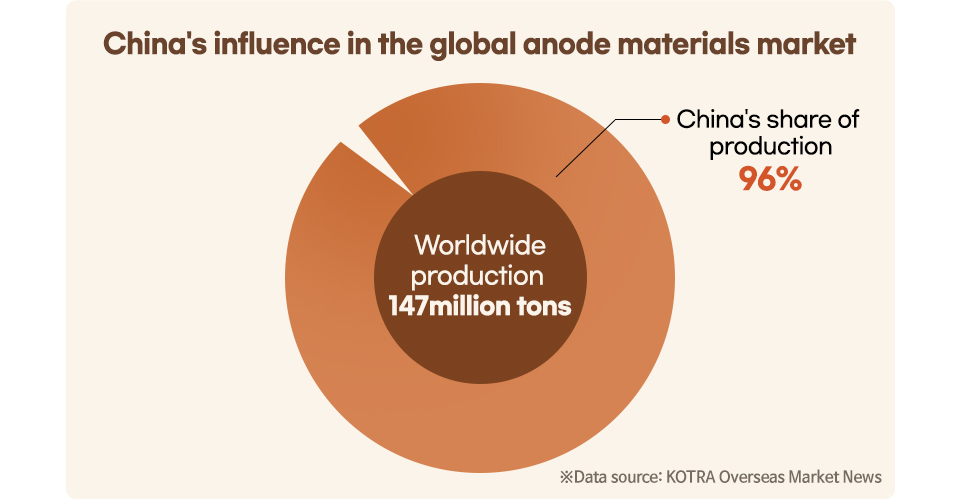
As orders increased from domestic companies that had imported anode materials from overseas, POSCO Future M increased its natural graphite anode material production capacity and expanded its product portfolio to include artificial graphite anode materials. Although artificial graphite anode materials are favored in the market for their long battery life and high-speed charging, commercialization is difficult because of high raw material costs. Until then, no companies produced them domestically, so only imports were available. When POSCO Future M succeeded in developing artificial graphite anode material first in June 2014, the use of this material increased as the electric vehicle market rapidly grew, and the company decided that it was the right time to produce artificial graphite anode materials and accelerated technological development proactively in response.

Manufacturing cost reduction and real-time quality management by introducing smart factory processes
Artificial graphite requires long and complex processes compared to natural graphite, and it is relatively difficult to control quality during production. POSCO Future M completely internalized all processes and introduced smart factory processes to reduce manufacturing costs and maintain customer trust through real-time quality control.
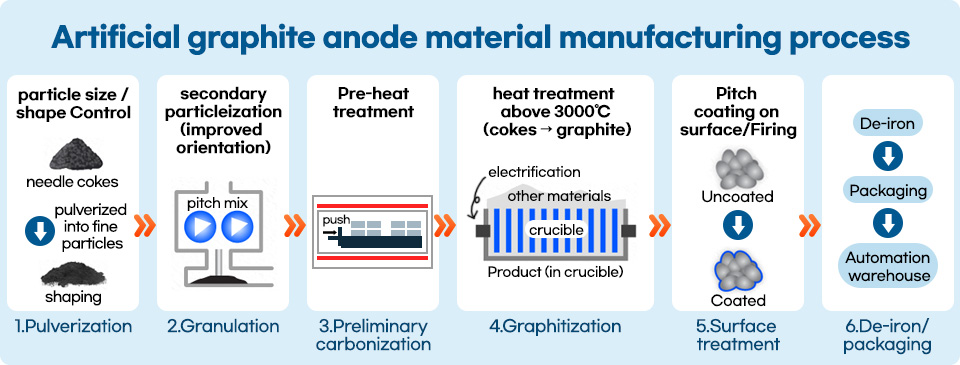
| • Pulverization: The process controlling the particle size of needle coke, a raw material • Granulation: The process of mixing needle coke and pitch • Preliminary carbonization: The process of carbonizing raw materials in advance to increase the productivity of the graphitization furnace • Graphitization: The process of converting raw material into artificial graphite by heat treatment at 3,000 ℃ or higher • Surface treatment: The process of coating the surface of artificial graphite evenly with pitch • De-iron/packaging: The process of completing and packaging the final product after post-processing, such as de-iron |
Let’s take a closer look at the production process of artificial graphite anode materials. The raw material for artificial graphite anode material is needle cokes, made by processing coal tar, a byproduct in the steelmaking process. There is a pulverizing process to adjust the size of needle coke particles, a granulation process of mixing needle coke and pitch during the pulverizing process, and a preliminary carbonization process of carbonizing the raw material before graphitization to increase productivity. Afterward, the raw material is thermally treated at 3000 ℃ or higher to convert it into artificial graphite, and the artificial graphite surface is coated evenly with pitch. Then, after post-processing, such as de-iron, the product is packed, which completes the production of artificial graphite anode materials in Korea.

Graphitization, which heat treats needle coke, the raw material, at a high temperature of 3,000 ℃ or higher is the core process and the most important technology that determines the quality and performance of the anode. It is very important to optimize the process conditions according to the raw material type and amount, and POSCO Future M has proprietary graphitization process technology for this.
The artificial graphite anode materials manufactured by POSCO Future M have the advantages of a longer battery lifespan due to their high structural stability and low impurity content and decreased fast charging time due to quicker lithium ion movement speed because of their isotropic structure.
Operational competitiveness is secured with a self-designed graphitization process
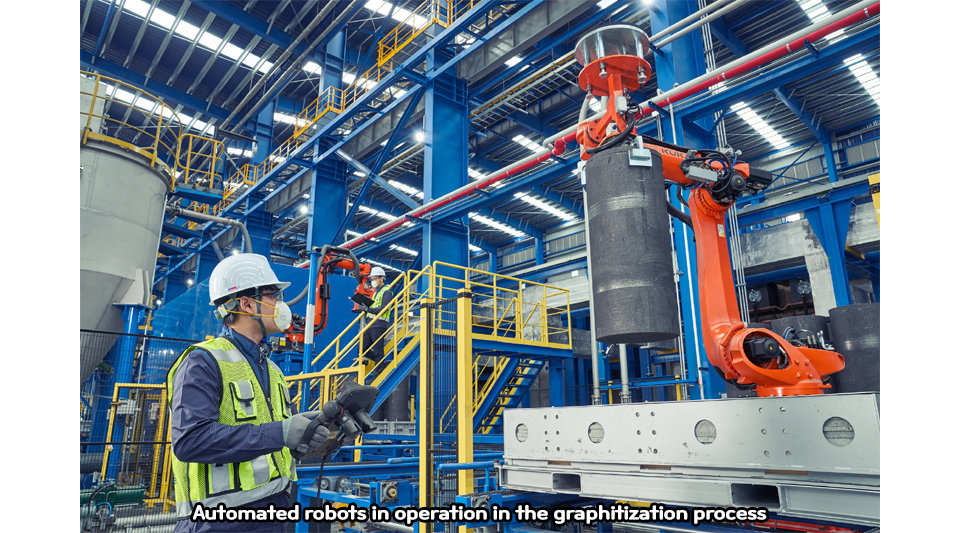

The graphitization process involves mixing raw materials in a crucible, placing them in a graphitization furnace, and heat-treating them at 3,000 ℃ or higher to produce graphite. Generally, when crucibles are put into and discharged from a graphitization furnace, people go directly into the furnace and perform various manual tasks, such as connecting the crane.
POSCO Future M designed the graphitization process automation system considering operator safety. Raw materials are transferred through a pipeline with strong air pressure, and robots put raw materials into crucibles and place them in the graphitization furnace. After being heat-treated at 3,000 ℃ or higher, artificial graphite is transferred through the pipeline to post-processes such as coating.
Value chain synergy effect to increase the resource circulation rate
Needle coke, the raw material for artificial graphite anode materials, is supplied by POSCO Future M’s subsidiary POSCO MC Materials. POSCO MC Materials produces needle coke by drying coal tar, a byproduct of coke manufacturing in the steelmaking process, at a high temperature. The localization of artificial graphite production technology has enabled POSCO to secure the steelmaking byproduct market and POSCO Future M to stably secure the raw material. It helps resource circulation and leads to the synergy effect of POSCO Group’s value chain.

Goal of increasing anode material production capacity
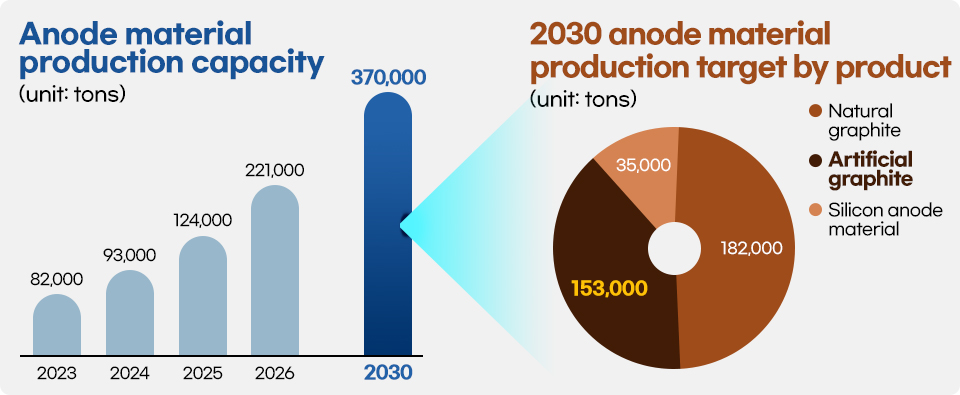
POSCO Future M plans to increase the annual anode material production capacity from 82,000 tons currently to 370,000 tons by 2030. Its goal is to maintain its No. 1 position in the global market outside China by having an annual production capacity of 182,000 tons of natural graphite anode materials, 153,000 tons of artificial graphite anode materials, and 35,000 tons of silicon anode materials by 2030.
First export of artificial graphite anode materials after localization
In December 2022, POSCO Future M signed a contract with Ultium Cells, a battery joint venture between U.S. GM and LG Energy Solutions, to supply artificial graphite anode materials worth approximately KRW 939.9 billion. The supply period is 6 years from 2023 to 2028. It is the first export of artificial graphite anode materials following localization. PSOCO Future M plans to secure its leadership in the artificial graphite anode material market by preemptively responding to increasing global demand, including expanding the supply chain in the battery industry following the enactment of the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act.

POSCO Future M is ready to fly higher with the localization of key battery materials!
Please follow us as we continue to pioneer the artificial graphite anode material market!
