Practically everything in the modern home, from the refrigerator to the electric toothbrush, runs on an electric motor. The global market for electric motors is worth tens of billions of dollars and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 4.2 percent from 2017 to 2025.
The ever-growing demand for electric motors can be attributed to several factors including the growing interest in eco-friendly and fuel-efficient motors and improved living standards in a number of densely-populated countries around the world. Plus, new innovations in home appliances are not only driving the demand for electric motors, it’s changing the way they are shaped, sized and put together.
So, how exactly do electric motors work?
An electric motor is in pretty much every electronic appliance. The motor is what turns electricity into mechanical movement. When an electric motor is charged with electricity, the axle, or metal rod turns and creates movement. The motor itself is powered by two opposing magnets – the permanent magnet and the electromagnet. When electric current is applied to the electromagnet, it pushes against the permanent magnet creating rotary or linear movement.
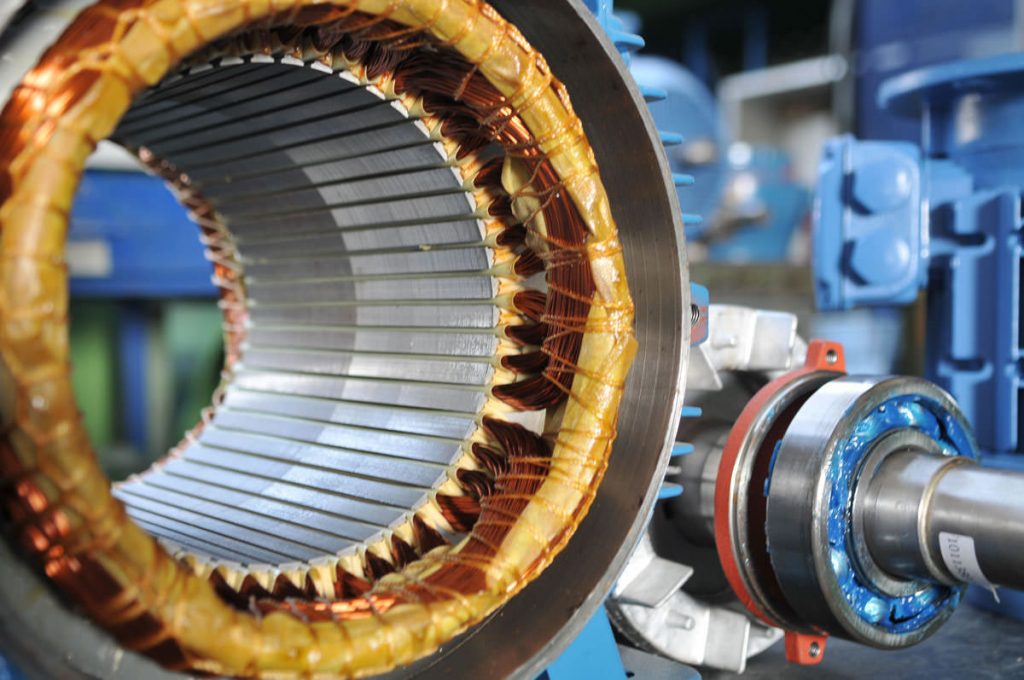
The inside of an electric motor. (Source: Stiavelli)
Many parts of electric motors are made of electrical steel, including the motor core. Electrical steel is an alloy of iron and silicon and can generate various magnetic properties. High-quality electric steel such as POSCO’s Hyper NO will have a small hysteresis curve that minimizes energy loss. POSCO’s technology also reduces core loss by 5 percent as well as motor noise by 5dB.
Electric Motors in Home Appliances
Home appliances currently account for about a third of total energy consumption and attribute to 45 percent of greenhouse gas emissions in an average household. Energy-efficient home appliances are in high demand due to increasingly stricter environmental regulations, consumers’ desire to save on utility bills as well as their desire to lower noise output from appliances such as dishwashers and dryers.
In order to maximize energy efficiency, engineers and manufacturers turn to high quality non-oriented electrical steel such as POSCO’s Hyper NO to meet consumer needs.
SEE ALSO: Why Electrical Steel Can Make All The Difference In EV Motors
Next Generation of Home Appliances
Aside from traditional home appliances, there is a growing number of innovative, next-generation home appliances that rely on high-quality electric motors for maximum efficiency, cost effectiveness and also range of movement.
These days, robots are part of the average household in the form of vacuums, personal home assistants, alarm clocks and more. Unlike traditional home appliances such as refrigerators and washing machines that are stationary, innovative robot appliances move in different directions. This is where actuators come in. Actuators are electric motors in a gearbox, and the gearbox essentially gives electric motors added torque, or rotational force, that allows the robot to move in a variety of directions, including twisting and turning.
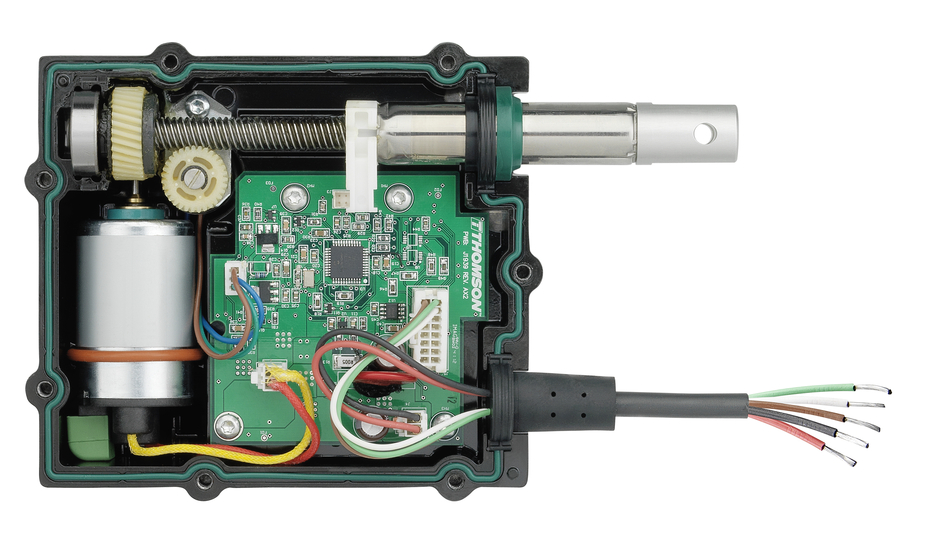
Actuators are what propels a variety of movement in robots. (Source: Motion Control Tips)
Moreover, engineers are now working with modular actuators to build robotic structures for a greater range of movement, speed and positions through segmented parts. Highly efficient, relatively low-cost and diverse actuators are coming together with AI sensors, voice recognition and smart controllers to breed a new generations of home appliances.
There are 3 different types of actuators based on how they are powered, and electrical actuators are most commonly found in home applications. Compared to the other types of actuators, electric actuators have lower speed and power, but are easy to install and control. Because they are often modular and can be applied for customized purposes, the resulting robots have a great range of motion to fit the new roles home robots are taking on.
Examples of Applications in the home
Here are some of the latest robots for the home that require advanced electric actuators and are changing the way people think of home appliances.
Aeolus Bot
The prototype for the Aeolus Bot was introduced at this year’s Consumer Electronics Show (CES) in Las Vegas. The robot can move around the nooks and crannies of the home learning different objects and places with its smart software. It can also retrieve different objects and clean the house using other home appliances.
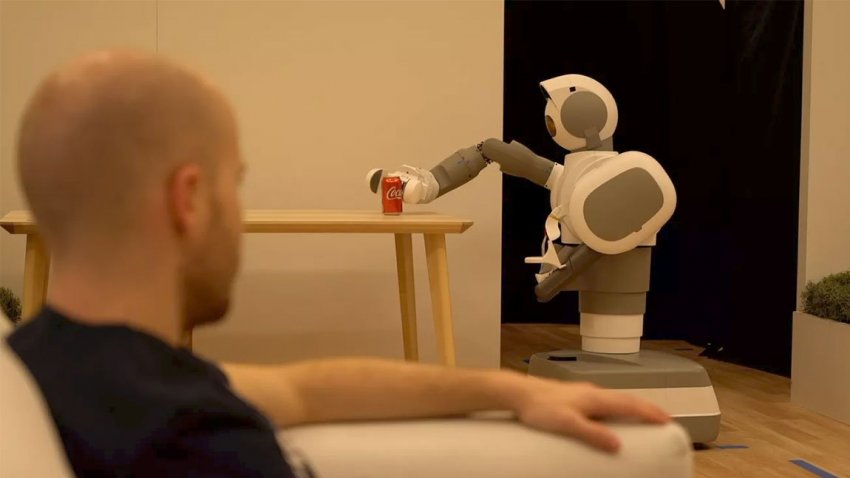
The Aeolus Bot responds to voice commands. (Source: Unbox Holics)
Not only that, Aeolus also has Amazon’s Alexa software, recognize its owner’s face and can alert family members of any disturbances.
Sony Aibo
Sony’s Aibo looks and moves like a dog. With its voice recognition software it can respond to commands, recognize faces and perform tricks. Although the furless bot may not be able to swim or jump the fence, it can pick up a objects, sit, roll over and move much more dynamically than other home robots.
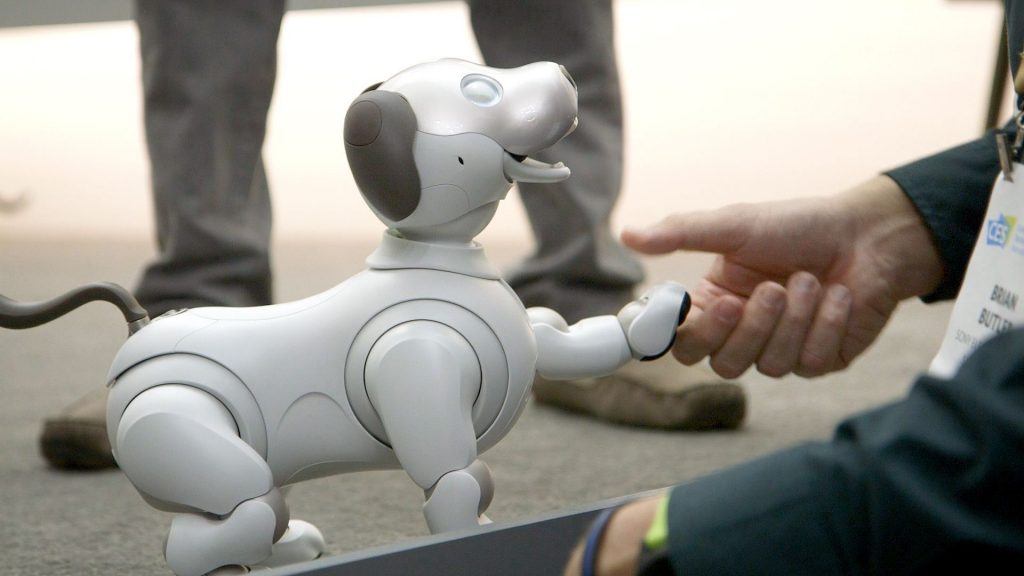

The Sony Aibo can do simple tricks on command. (Source: The Verge)
The changing face (and shape) of home appliances is putting actuators to full use with their wide range of movement, speed and positions. Highly-efficient electric motors and actuators will continue to be in high demand as new innovations in home appliances and robots keep rolling out.
Cover photo courtesy of GE Reports.
- actuators
- Aeolus Bot
- Aibo
- CES
- Consumer Electronics
- consumer electronics conference
- Consumer Electronics Show
- electric actuators
- electric motors
- electrical motor
- Electrical Steel
- electricity
- electromagnet
- Electronics Show
- energy
- global market
- home appliances
- hyper no
- Hyper NO posco
- innovations
- Las Vegas
- POSCO
- posco electrical
- posco electrical steel
- posco motor steel
- robot
- robot motor
- smart
- software
- Sony Aibo
- steel
