
POSCO Group, which holds core capabilities across the entire value chain—from energy business development to materials supply and Engineering, Procurement & Construction (EPC)—is accelerating its energy transition strategy by consolidating business capabilities and synergies in preparation for the upcoming decarbonization era. In particular, the Infrastructure Division, which includes diverse business units such as energy, construction, infrastructure, DX, and logistics, is expanding its energy transition initiatives centered on POSCO International. These efforts include advancing hydrogen co-firing power generation, which is emerging as a realistic power generation option during the decarbonization process, securing renewable energy sources such as onshore/offshore wind power and solar power, and accelerating the development of high-quality energy steel. Let’s take a closer look at POSCO Group’s energy transition strategy toward decarbonization.

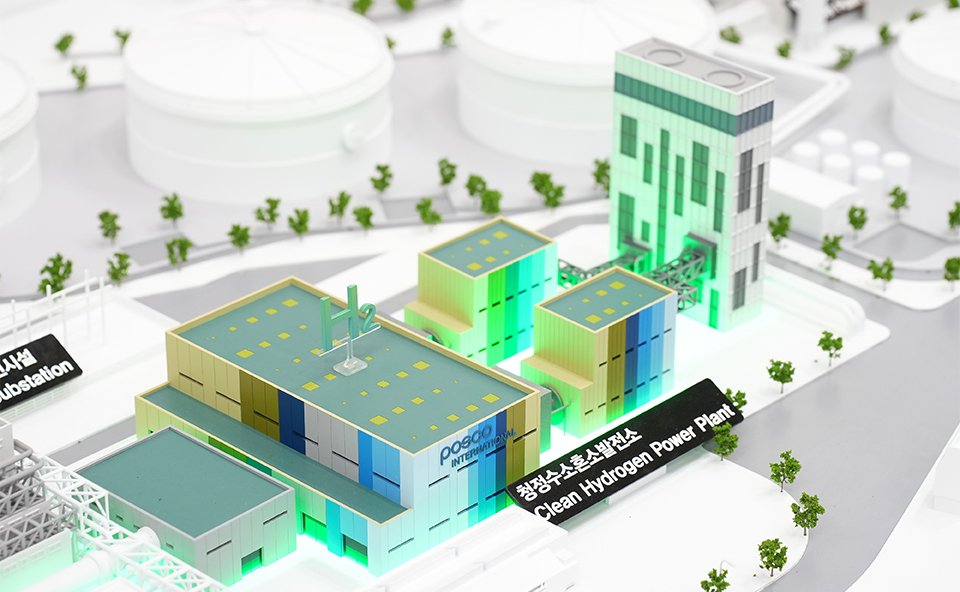
POSCO International, which operates the 3.4 GW Incheon LNG complex power plant, is advancing a hydrogen co-firing initiative that replaces 20% of the LNG fuel used in its power plant with clean hydrogen. Hydrogen co-firing power generation refers to a method of generating electricity by combusting a mixture of natural gas (LNG) and hydrogen in a gas turbine*. Increasing the hydrogen ratio reduces CO₂ emissions generated during the power generation process. As it enables the use of existing power generation facilities while reducing carbon emissions, hydrogen co-firing power generation is emerging as a practical power generation method and a transitional bridge toward decarbonization.
*Gas turbine: A core component of combined cycle power plants that generates electricity by combusting fuel and converting high-temperature, high-pressure gas into rotational force. It can operate not only on natural gas but also on fuels such as hydrogen, offering flexibility for diverse energy mixes.
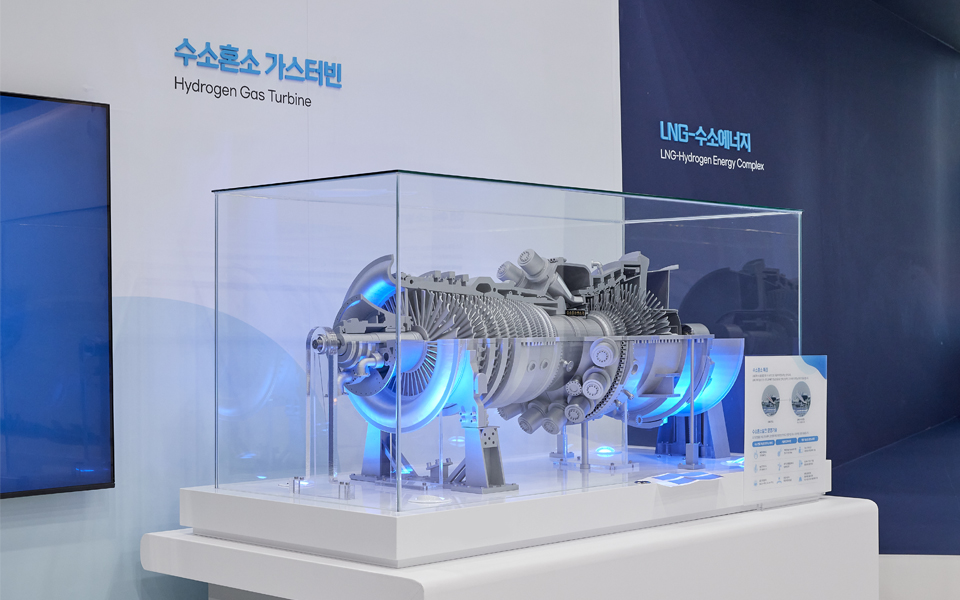

▲ Scale model of a gas turbine for hydrogen co-firing power generation under development by POSCO International.
POSCO International plans to replace Units 3 and 4 of the seven combined cycle power units at the Incheon LNG complex power plant with high-efficiency power generation facilities capable of using clean hydrogen fuel. Through hydrogen co-firing, the company expects to reduce CO₂ emissions by up to approximately 35%. Starting with Units 3 and 4, POSCO International will gradually transition additional facilities and increase the hydrogen co-firing ratio, ultimately aiming to operate the plant as a 100% hydrogen-based power generation facility by 2050.
Furthermore, to ensure a stable supply of clean hydrogen—which is essential for operating hydrogen co-firing power generation—POSCO International is actively participating in global clean hydrogen production projects in North America, the Middle East, and Australia. It is also developing transport and storage infrastructure using ammonia. In January 2024, POSCO International, together with POSCO Holdings, signed the “Strategic Cooperation Agreement (SCA) for a Joint Investigation of Clean Hydrogen Production Business” with ADNOC, an oil corporation run by Abu Dhabi, UAE. Through such partnerships, the company is proactively building the clean hydrogen supply infrastructure required for hydrogen co-firing power generation.

Photo source: POSCO International |
Incheon LNG Combined Cycle Power Plant Operated by POSCO International
POSCO International operates a total of seven combined cycle power generation units, with a facility capacity of 3,412 MW, accounting for about 10% of the metropolitan area’s power generation facilities. With very short start-up/shutdown times, the plant can respond quickly to fluctuations in national power demand, contributing to the country’s energy security. POSCO International applies IoT and big data to its power plant operation technology, running it as a smart power plant. |

To address the global climate crisis, governments and corporations around the world are accelerating the transition to renewable energy sources such as offshore wind power and solar power. POSCO Group is also expanding its renewable energy business by integrating its differentiated capabilities across project operation, EPC, and materials supply, creating strong synergies.
POSCO International Operates Onshore and Offshore Wind Power Farms and Solar Power Plants

▲ View of the Sinan Green Energy onshore wind farm operated by POSCO International.
POSCO International is leading the future energy transition by leveraging the abundant onshore and offshore resources of Sinan, Jeollanam-do. Shinan Green Energy, a subsidiary of POSCO International, has installed 20 wind turbines in Jaeun-myeon, an area with excellent wind conditions, operating an onshore wind farm with a total capacity of 62.7 MW since 2016. The electricity generated is sufficient to supply approximately 31,000 households in the Sinan and Mokpo regions, reducing CO₂ emissions by roughly 49,000 tons annually.
As Shinan Green Energy expands its renewable energy initiatives centered around Sinan, Jeollanam-do, it is also actively engaging in community contribution activities. Since commercial operations began in 2017, the company has pledged 1.5% of annual revenue to Sinan’s development fund for 10 years, and has donated KRW 800 million to support the construction of a multifunctional community center—demonstrating its commitment to coexistence with the local community alongside renewable energy production.
Their wind power market expansion continues offshore as well. In 2017, POSCO International obtained approval to develop a 300 MW offshore wind farm west of Jaeundo Island in Sinan and has since continued its development efforts. The company is further expanding its offshore wind power business through increased collaboration with global industry leaders.
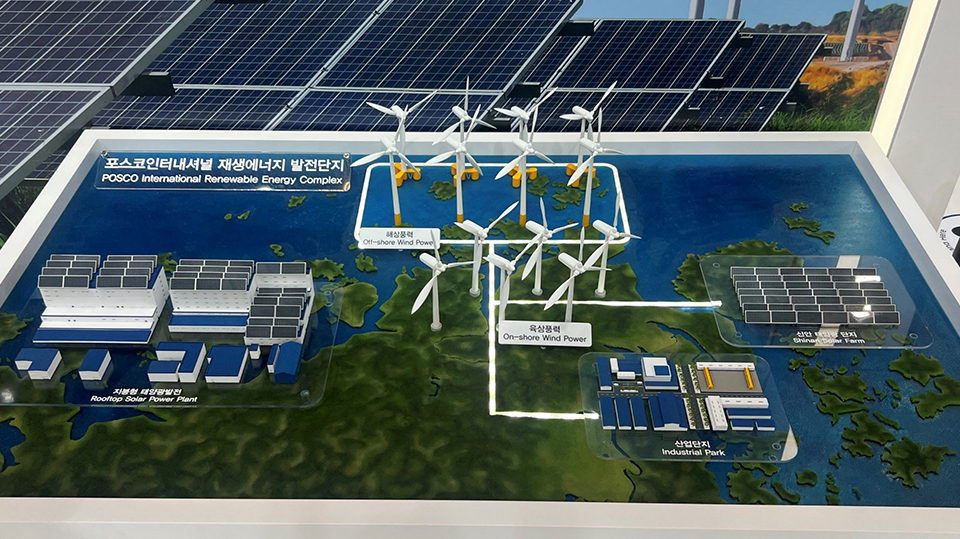
▲ Model of POSCO International’s renewable energy complexes displayed at the 2025 International Climate Industry Expo, showcasing onshore and offshore wind farms and solar power facilities in Sinan, Jeollanam-do
POSCO International also operates a large-scale 14.5 MW solar power complex in three phases across a former salt field in Palgeum-myeon, Sinan. By utilizing unused salt field land, the solar complex minimizes environmental impact while taking advantage of the high solar radiation characteristic of salt pans to generate efficient renewable energy. It produces approximately 18,000 MWh of electricity annually, enough to power around 5,300 households, which translates to a reduction of about 7,600 tons of CO₂ emissions and an environmental benefit equivalent to planting 2.2 million pine trees each year.
▲ Introduction video of POSCO International’s onshore and offshore wind farms and solar power complexes in Sinan, Jeollanam-do (Video source : POSCO International YouTube)
POSCO E&C Constructs the Ulsan Firefly Floating Offshore Wind Power Complex
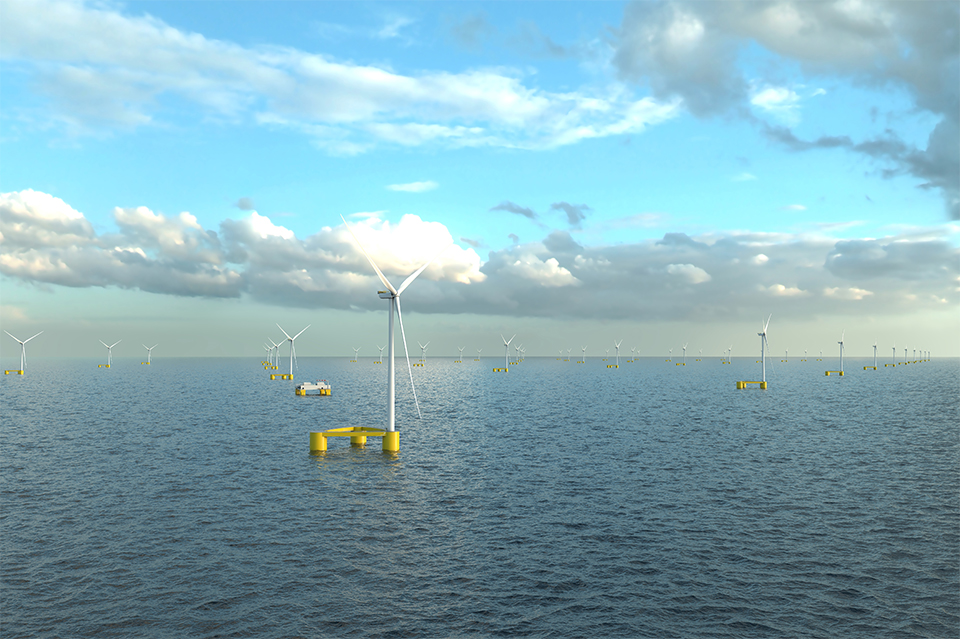

▲ Rendering of the Ulsan Bandibbul floating offshore wind farm under development by POSCO E&C and Equinor.
POSCO E&C, drawing on extensive experience in offshore construction and power plant development, is advancing into the offshore wind power sector through collaboration with global offshore wind power specialists and domestic academic institutions. In 2023, it signed an MOU with Norway’s DNV to secure optimized design technology for fixed and floating offshore wind power substructures. In September 2024, it strengthened its competitiveness further by partnering with Equinor, Norway’s state-owned energy company and the only global developer with proven experience in floating offshore wind power.*
*Floating offshore wind power: Unlike conventional fixed offshore wind power, which installs foundation structures on the seabed, floating offshore wind power uses buoyant structures that support wind turbines on the ocean surface. This allows installation in deeper waters where stronger and more stable winds can be harnessed, minimizes seabed construction, reduces environmental impact, and enables more flexible installation and relocation.
POSCO E&C, in collaboration with Equinor, is constructing a 750 MW floating offshore wind power complex through the Ulsan “Firefly” offshore wind power project. The large-scale project involves installing fifty 15 MW wind turbines approximately 70 km east of Ulsan Port. POSCO E&C is strengthening its construction capabilities through activities such as Front-End Engineering Design (FEED) and conceptual design for onshore transmission lines.
Additionally, POSCO E&C is enhancing collaboration with POSCO to strengthen technological competitiveness and cost efficiency in offshore wind power. The company is particularly focused on independently developing floater technology using POSCO’s high-performance thick steel plates. Internalizing the technology for key components and structures is expected to serve as a crucial foundation for achieving leadership not only in the domestic market but also in the global offshore wind power market.
Furthermore, POSCO Group is accelerating the energy transition by collaborating with global renewable energy companies to lead and strengthen competitiveness in the offshore wind power industry.
POSCO Future M Produces Renewable Energy through Rooftop Solar Panel Structures
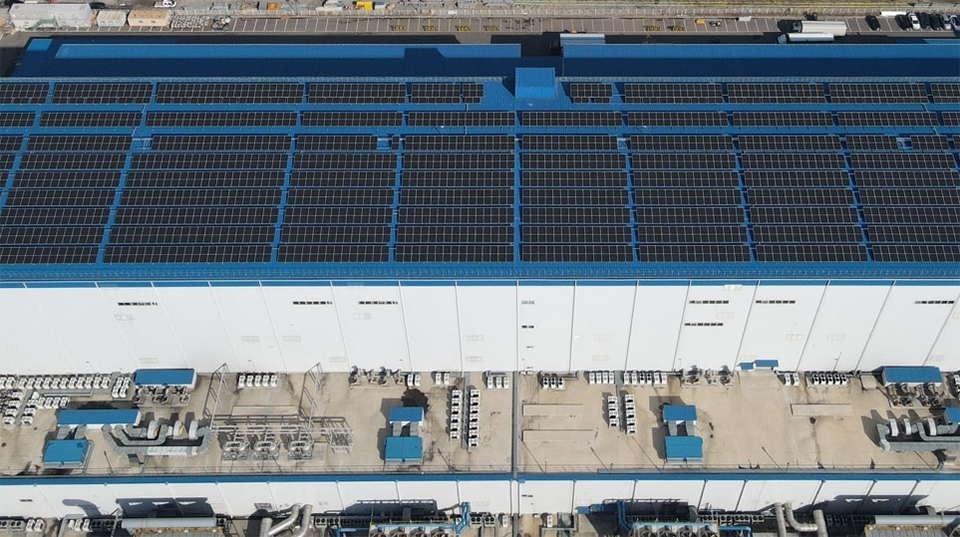

▲ Solar power facilities at POSCO Future M’s Gwangyang cathode plant, installed in February 2024 in collaboration with POSCO International. Since 2021, POSCO Future M has also operated rooftop and parking lot solar installations at its Sejong anode plant, producing 209 MWh of renewable energy annually.
POSCO Group is proactively expanding renewable energy production and usage across its subsidiaries. In February 2024, POSCO Future M, in collaboration with POSCO International, installed 2.2 MW of rooftop solar panels at its Gwangyang cathode material plant. POSCO International produces 2.6 GWh of renewable energy annually from these panels and secures Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs), which POSCO Future M purchases to support its RE100 commitments—creating a sustainable circular system.
Recently, POSCO Future M signed an agreement with SK Innovation E&S to jointly promote a solar power generation project. SK Innovation E&S will install 2.5 MW of solar panels on the factory rooftops and parking lots, generating 2.8 GWh of renewable electricity annually. POSCO Future M plans to purchase this electricity for plant operations, expecting to reduce carbon emissions by approximately 1,300 tons per year.
Going forward, POSCO Future M plans to review additional installations of solar power generation facilities at sites such as its dedicated Gwangyang NCA cathode material plant, and to diversify its renewable energy procurement methods through Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) and REC purchases.

Materials also play a critical role in POSCO Group’s diverse energy businesses. Renewable energy, Energy Storage System (ESS), LNG, hydrogen, and Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS) projects require specialized steel products tailored to their unique operational environments. Because temperature, pressure, and corrosion conditions vary greatly by application, general structural steel cannot ensure adequate performance or safety. POSCO produces and supplies high-quality, proprietary energy steel designed specifically for various domestic and international energy applications.
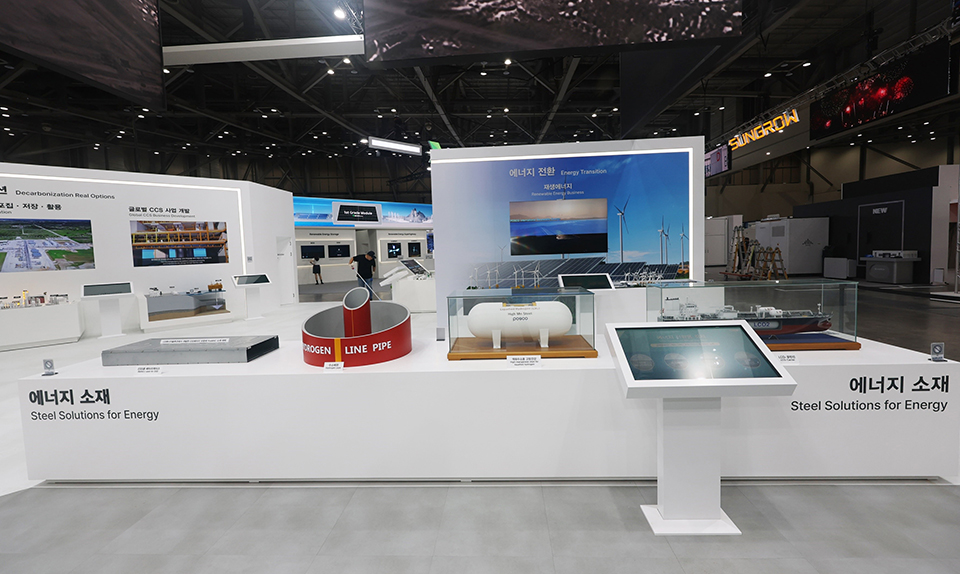

▲ POSCO’s energy steel products at the 2025 International Climate Industry Expo — PosMAC for ESS, steel for hydrogen pipelines, and high-manganese steel.
A representative example is PosMAC (POSCO Magnesium Alloy Coating Product), an ultra-corrosion resistant alloyed steel plate that applies an alloy coating layer containing magnesium (Mg) and aluminum (Al). It offers superior strength and durability compared to conventional galvanized steel sheets. Its excellent corrosion resistance extends product lifespan by reducing replacement cycles, thereby reducing raw material usage and lowering carbon emissions during manufacturing and transportation. POSCO plans to expand the use of PosMAC in key ESS components, such as battery cases, racks, and BPU cases, through collaboration with customer companies.

▲ LNG storage tank model built with POSCO high-manganese steel.
POSCO’s high-manganese steel—developed as a world first—has higher strength than stainless steel and remains intact even at -196°C, making it suitable for safely storing and transporting LNG and liquefied hydrogen. POSCO is also strengthening market competitiveness through the development of additional energy-related materials, including steel for hydrogen pipelines that resist high pressure and hydrogen embrittlement, and LT-FH36 steel for liquefied CO₂ carriers. POSCO Group plans to build a global energy transition ecosystem by expanding the development and production of high-quality special steel made with its proprietary technologies.
POSCO Group’s energy transition strategy goes beyond short-term carbon reductions and focuses on building a sustainable industrial ecosystem. We look forward to your continued interest and support as POSCO Group advances toward the decarbonization era and drives its energy transition initiatives forward!
