l POSCO envisions becoming a green hydrogen company leading the hydrogen economy with the ultimate target to achieve 30 trillion KRW in hydrogen sales by 2050
l CEO Jeong-Woo Choi remarks, “POSCO will contribute to establishing a domestic hydrogen ecosystem for a carbon-neutral society”
l The company is to place hydrogen business as one of its growth engines for the group and put together group capabilities to create a value chain consisting of production, transport, storage, and application
l POSCO is to launch a business division in January next year, and as an initial project, the company will construct hydrogen stations in the local areas of the steelworks and change steel transport vehicles into hydrogen vehicles
POSCO (CEO Jeong-Woo Choi) presented a blueprint on how to become a “green hydrogen company that leads the hydrogen economy” and pioneer decarbonization. To materialize this vision, POSCO will establish a hydrogen production capacity of 5 million tons by 2050 and achieve 30 trillion KRW in hydrogen sales.
In specific, POSCO will focalize on equipping itself with production capabilities and core technologies, including technology to produce hydrogen by electrolyzing water and technology to extract hydrogen by 2030, and nurture the hydrogen business as the group’s growth engine to take the lead in the future hydrogen market.
POSCO CEO Jeong-Woo Choi said, “POSCO will work on producing and supplying hydrogen, a major clean energy of the future.” He added, “We will contribute to enhancing the national hydrogen ecosystem towards carbon neutrality.”
The annual domestic demand for hydrogen, the next-generation source of clean energy, is expected to increase to 1.94 million tons in 2030 and over 5.26 million tons in 2040. The field of application will also expand from the current petrochemical industry to transport and power generation areas. Accordingly, the Korean government has launched the Hydrogen Economy Committee and declared the Green New Deal policy to promote the transition to a hydrogen economy.
Currently, POSCO possesses an annual hydrogen production capacity reaching 7,000 tons, utilizing the Cokes Oven Gas during the steelmaking process and natural gas (LNG). Among them, around 3,500 tons of byproduct hydrogen are extracted and used to control temperature and prevent oxidation while steelmaking. Also, POSCO is furnished with capabilities necessary for producing and applying hydrogen, such as developing the world’s first steel products for hydrogen fuel cell separators and supplying them to domestic hydrogen carmakers.
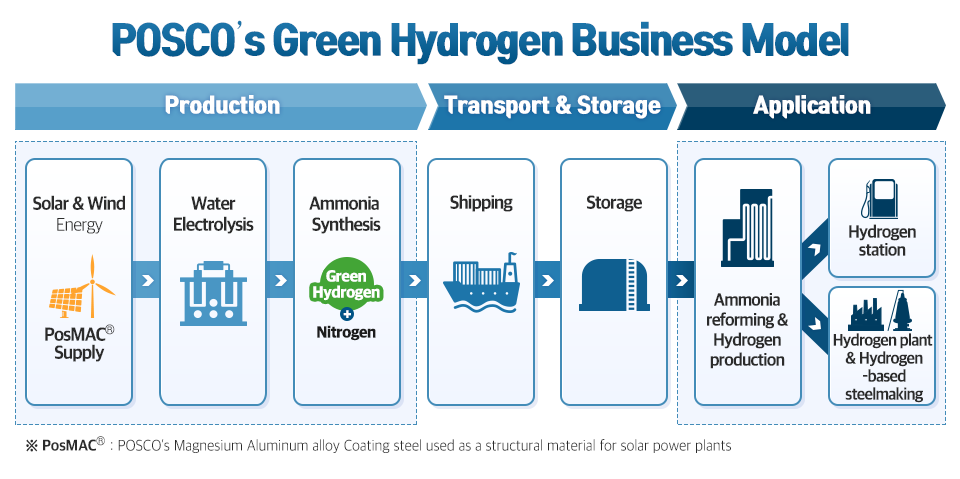
In the future, POSCO will conduct research on hydrogen-based steelmaking technology and strengthen its capabilities by developing steel products for producing, transporting, storing, and applying hydrogen, increasing byproduct hydrogen production facilities, and developing core technologies for hydrogen production. Furthermore, the company also plans to pursue large-scale investments by exploring various business opportunities, such as distributing and establishing infrastructure for ‘Green Hydrogen,’ and participating in ‘Green Hydrogen’ projects.
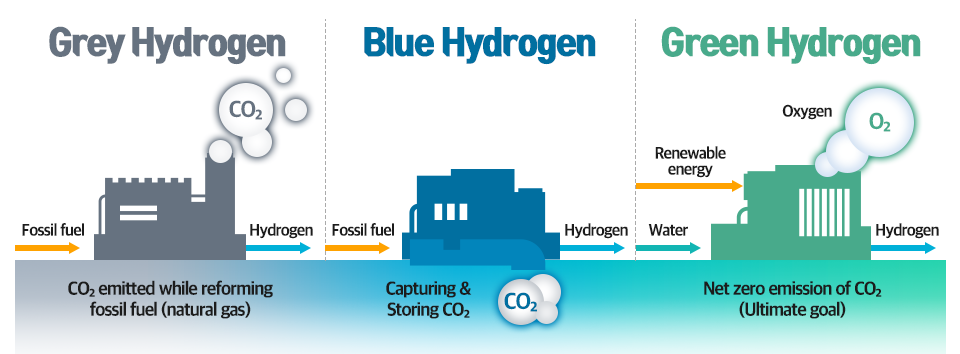
In this respect, POSCO intends to boost the production capacity of by-product hydrogen to 70,000 tons by 2025 and to produce up to 500,000 tons of ”Blue Hydrogen*” by 2030 in partnership with global companies. The company also plans to complete 2 million tons of production capacity of “Green Hydrogen**” by 2040 and then expand the production to 5 million tons by 2050.
* Blue Hydrogen: Hydrogen produced with fossil fuels, such as natural gas. The carbon dioxide generated during the production process of hydrogen is captured, separated, and stored underground.
** Green Hydrogen: Hydrogen produced by water electrolysis based on renewable energy.
POSCO also plans to construct a “Green Hydrogen”-based steelworks by 2050 and open an era of decarbonization and hydrogen in the steel industry. Once the hydrogen-based steelmaking technology becomes commercialized, the annual amount of “Green Hydrogen” required is expected to reach a maximum of 3.7 million tons, hence placing POSCO as the largest demander and producer of hydrogen.
Furthermore, to secure core technologies necessary for the production and transport of “Green Hydrogen,” POSCO will cooperate with domestic and overseas research institutes and promote partnerships with global companies. It will also develop ammonia hydrogen extraction technology, a key technology applied for the transport and storage of hydrogen. Ammonia is a compound of hydrogen and nitrogen and is considered an efficient and economical carrier since it is easy to transport and store.
As an initial project, POSCO will build infrastructure, such as hydrogen stations in adjacent areas of the steelworks, and change steel transport vehicles and other vehicles used by the company into hydrogen vehicles. These actions are expected to cultivate a hydrogen ecosystem based on steel logistics, hence creating a secure base demand. Currently, there are around 1,500 large trucks in POSCO for transporting steel products, and when including temporarily operated ones, the figure reaches 5,000 annually.
In addition, POSCO plans to put together group capabilities to create a value chain consisting of production, transport, storage, and application. POSCO International will utilize its overseas network to participate in the government’s hydrogen project and overseas hydrogen projects, while POSCO Energy will build a terminal to store hydrogen exclusively and replace the current LNG turbine power with hydrogen turbine power in stages from 2030. POSCO E&C will take the role of building hydrogen urban development projects and projects necessary for hydrogen storage and transport.
Meanwhile, in an action to initiate the hydrogen business in full swing, POSCO plans to launch a new business division in January next year and promote R&D cooperation with domestic and overseas research institutes, centering on RIST (Pohang Institute of Industrial Science and Technology).
